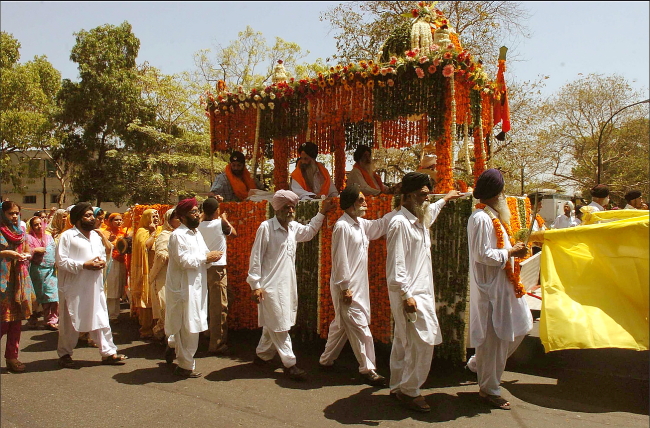
SUNDAY, APRIL 21: Around the world today, Indian communities and Sikhs are celebrating Vaisakhi (or Baisahki; spellings vary), an occasion for colorful processions and public festivals. From the Vancouver Vaisahi Parade and Festival (CBC News has a video of this year’s celebration, here) to London (read more from the BBC) to New York (watch interviews and more in a video of this year’s celebrations, courtesy of Spectrum News 1) Sikhs worldwide are enjoying the spirit of this holiday.
Did you know? The festival’s name refers to a month in the traditional Hindu calendar: Vaisakha.
In India, Vaisakhi holds varying meanings in different regions. First, this was an ancient agricultural festival in the Punjab; a time of prayers for bountiful crops. In the Punjab region (and among families with Punjabi roots around the world), it is an ancient agricultural festival and a time for prayers for bountiful crops; one custom is an energetic dance called Bhangra, which dates back centuries. Hundreds of years ago, while farmers were preparing to reap a harvest of wheat at this time of year, men would pause to perform this dance. The Bhangra has moved through several different eras and forms, according to scholars of Indian folklore. Today, there is a modern revival of the practice, complete with colorful costumes, that is often performed at Vaisakhi festivals.
FOR SIKHS: THE KHALSA
Though celebrated by many, Vaisakhi holds particular significance for Sikhs who, in 1699, established the Khalsa. On Vaisakhi Day in 1699, Guru Gobind Singh emerged from a tent before thousands, asking for five volunteers willing to give their lives. Armed with a sword, the Guru took in the first volunteer; a few minutes later, the Guru emerged from the tent again, his sword covered in blood. By the time five volunteers had come forward, the Guru revealed his true intentions: to call forth a “Beloved Five,” who would be baptized into a new order known as the Khalsa. The five volunteers exited from the tent—unharmed and wearing turbans. To this day, Sikhism incorporates a readiness to fight for justice by protecting the vulnerable.
SIKH VAISAKHI: PILGRIMAGES & SERVICE
Tens of thousands of Sikhs journey to holy sites each year for Vaisakhi—one city even bears the name of the first Sikh Guru, Nanak. Thousands more flock to the birthplace of the Khalsa, as well as to the famed Golden Temple at Amritsar. Sikhs in the United States can travel to Los Angeles, California for an entire day of Kirtan (spiritual music based on the holy book, Guru Granth Sahib) and a large-scale parade; in Manhattan, New York City, Sikhs flood into the streets to perform seva (selfless service) of charity.
Further north, Canadians in British Columbia parade through the streets for Vaisakhi, often drawing hundreds of thousands of attendees to the festivities. The UK boasts its own sizeable Sikh population, though most adherents can be found in west London; events there draw tens of thousands of attendees.